The Historical Significance of Piraminds
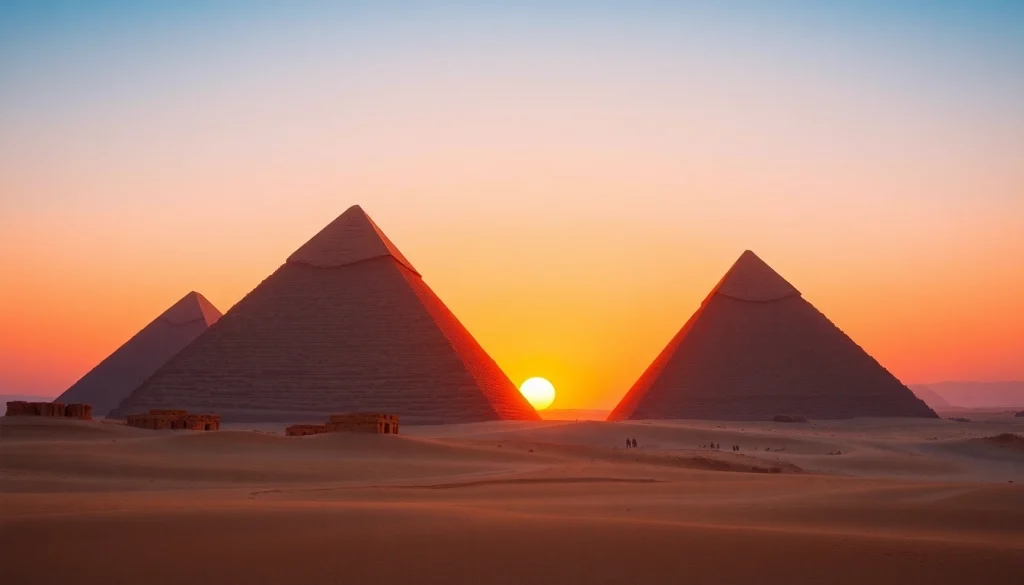
The piraminds, often misconceived solely as mere tombs, stand as monumental testaments to the ingenuity and persistent spirit of ancient civilizations. Constructed primarily during the Old and Middle Kingdoms of Ancient Egypt, these architectural wonders served multifaceted purposes, from tombs for pharaohs to centers of worship, reflecting the social, political, and spiritual values of their time. Understanding the piraminds goes beyond their physical appearance; they encapsulate a rich tapestry of human history, artistry, and cosmic beliefs.
The Origins of Piraminds
The origins of piraminds can be traced back to earlier mastaba tombs, which were flat-roofed, rectangular structures. The evolution to the step pyramid, the first monumental stone structure, exemplified advanced engineering skills and ambitious architectural vision. The Step Pyramid of Djoser at Saqqara is often regarded as the first true piramid, laying the foundation for the later, more refined shapes seen in Giza.
Piraminds in Ancient Civilizations
Throughout ancient civilizations, piraminds embodied more than burial sites; they symbolized the connection between the earth and the divine. The Egyptians believed that these structures facilitated the pharaoh’s ascension to the afterlife, where they would be deified among the gods. In this context, the piraminds became crucial to the state’s ideology, linking governance with the divine and emphasizing the eternal nature of the soul. Other cultures, like the Nubians, also adopted the concept of pyramids, creating their versions that reflect localized architectural styles and cultural values.
Cultural Impact of Piraminds in Modern Times
Today, piraminds remain a focal point of cultural significance and tourism in Egypt. They inspire countless studies in archaeology, history, and architecture, revealing the complexities of human endeavor and societal evolution. Moreover, they have influenced modern culture, lending their iconic shape to various forms of art, architecture, and media, symbolizing mystery and grandeur worldwide.
Architectural Mastery of Piraminds
The construction and design of piraminds are marvels of ancient engineering. Their architectural mastery challenges our understanding of ancient technology and resource management, demonstrating a sophisticated approach to construction that blends artistry with mathematical precision.
Construction Techniques Used in Piraminds
The construction techniques employed in the piraminds involved innovative methods for their time. Studies suggest that large blocks of limestone, granite, and basalt were quarried and transported using sledges lubricated with water. Ramp systems were likely employed, allowing workers to move heavy stones upward with remarkable efficiency. Recent theories propose the use of a circular ramp that twisted around the piramid’s exterior, facilitating the ascent of materials.
Materials and Tools for Building Piraminds
The materials used for constructing piraminds were meticulously chosen, utilizing local stones such as limestone for core structures and granite for casing stones. Workers employed tools made from copper and stone, with chisels and hammers reflecting significant craftsmanship that allowed them to shape and fine-tune stone blocks accurately. The precision in the fitting of these stones is a testament to their experience and skilled labor.
Innovations in Piramids Design and Architecture
Innovations in design are evident in the gradual transition from the stepped designs to the smooth surfaces of the Giza pyramids. These advancements showcased not only aesthetic appeal but also improved structural integrity. The Great Pyramid of Giza, for instance, features a sophisticated layout with chambers and passageways that demonstrate advanced understanding of spatial dynamics.
Myths and Mysteries Surrounding Piraminds
The piraminds are steeped in myths and mysteries that have captivated researchers and enthusiasts alike. From their construction to their purpose, various misconceptions and speculative theories have arisen, adding layers of intrigue to these monumental structures.
Common Misconceptions About Piramids
One prevalent misconception is that piraminds were built by slaves. In reality, a large workforce composed of skilled laborers, craftsmen, and volunteers significantly contributed to their construction, often motivated by religious and nationalistic fervor. Additionally, the belief that piraminds were solely tombs for pharaohs discounts their role as complex structures with multifunctional purposes, including religious and ceremonial significance.
Unexplained Phenomena Linked to Piramids
Various unexplained phenomena surround piraminds, from their precise alignment to celestial bodies to reports of strange acoustic properties within their chambers. Some researchers suggest that the alignment of the pyramids with the Orion constellation and their geographic placement may have cosmic significance, linking them to ancient Egyptians’ beliefs about the afterlife and their relationship with the heavens.
Documented Discoveries Inside Piramids
Exploration of piraminds has led to numerous discoveries, including artifacts, hieroglyphs, and architectural features that provide insight into ancient Egyptian society. Recent advancements in non-invasive technologies, such as muon tomography, have revealed hidden chambers within the Great Pyramid, igniting further interest in uncovering the mysteries lurking behind their limestone facades.
Tourism and Preservation of Piraminds
As one of the most recognizable symbols of ancient civilization, piraminds draw millions of tourists every year. However, the preservation of these structures poses significant challenges that necessitate careful management and conservational efforts.
Visiting Piramids: What to Expect
Visitors to the piraminds can expect to encounter not only awe-inspiring architecture but also a rich narrative of ancient history. Guided tours often provide context, exploring the significance of the structures, their construction, and their place in Egyptian mythology. The surrounding landscape complements the experience, as visitors can appreciate the piramids against the backdrop of the Giza plateau and the sprawling desert.
Conservation Efforts for Piramids
Conservation efforts for the piraminds involve multidisciplinary approaches incorporating archaeology, environmental science, and tourism management. Initiatives include stabilizing the structures, mitigating environmental damage, and controlling the impact of tourism. Collaborative programs between governments and international organizations aim to raise awareness and funds for ongoing preservation efforts.
The Future of Piraminds as Tourist Attractions
The future of piraminds as tourist attractions hinges on sustainable practices that balance preservation with public engagement. Plans to improve visitor facilities, enhance educational initiatives, and implement advanced conservation techniques are essential for maintaining their legacy for future generations. By promoting responsible tourism, the piraminds can continue to inspire and educate long into the future.
FAQs About Piraminds
What are the most famous piraminds in Egypt?
The most famous piramids in Egypt include the Great Pyramid of Giza, the Pyramid of Khafre, and the Pyramid of Menkaure, all located on the Giza Plateau.
How were the piraminds built?
Piraminds were built using large limestone and granite blocks, transported through innovative techniques like sledges and ramps, with skilled labor ensuring precision in construction.
Can you enter the piraminds?
Yes, many piraminds allow access to their interior chambers, though some may have restrictions for preservation reasons and to ensure safety for visitors.
What do the piraminds symbolize?
Piraminds symbolize the Pharaoh’s power and their connection to the divine, serving as monumental gateways for the soul’s journey to the afterlife.
Are there services for tourists at the piraminds?
Yes, there are various services for tourists, including guided tours, informational signage, visitor centers, and facilities catering to the needs of visitors at the piramids.